
A blockchain is a decentralized, public ledger that records and confirms all transactions that took place in that network. Blockchain is widely known for the vital role it plays in the crypto network. Without it, a crypto network will collapse in no time. They are immutable, and hence ideal for boosting security in a crypto economy. However, they are not exclusive for cryptocurrency uses. They are also used by major tech companies to store their data so it is not manipulated by any external entity. In this article, we will look more into blockchain technology, how it works, and also the various applications of blockchain.
A blockchain is quite similar to a spreadsheet or database, which you use to enter and store data. The main thing that differentiates blockchain from them is its accessibility and structure. In blockchain technology, there are various programs referred to as scripts that are used for inputting, storing, and accessing data. Since the blockchain is a distributed ledger, multiple copies of the data are stored within different nodes that are present on the network. If there is a mismatch is found in the data stored in them, then we can conclude that some sort of tampering has taken place.
For instance, if we take the BTC blockchain, it collects and stores the data in a 4MB file called blocks. Once the full storage of the blocks is utilized, the data stored in it is run through a hash function. The output of this process gives us a hexadecimal number called block header hash. This is then provided to the next block header in the line and is encrypted along with the data that is already stored in it. This results in a “chain of blocks”, hence its name.
Transaction Process In a Blockchain
A blockchain transaction is a secure and decentralized process that is mainly used to verify and record a transaction that takes place on the network. Here is the list of steps that are executed during the transaction.
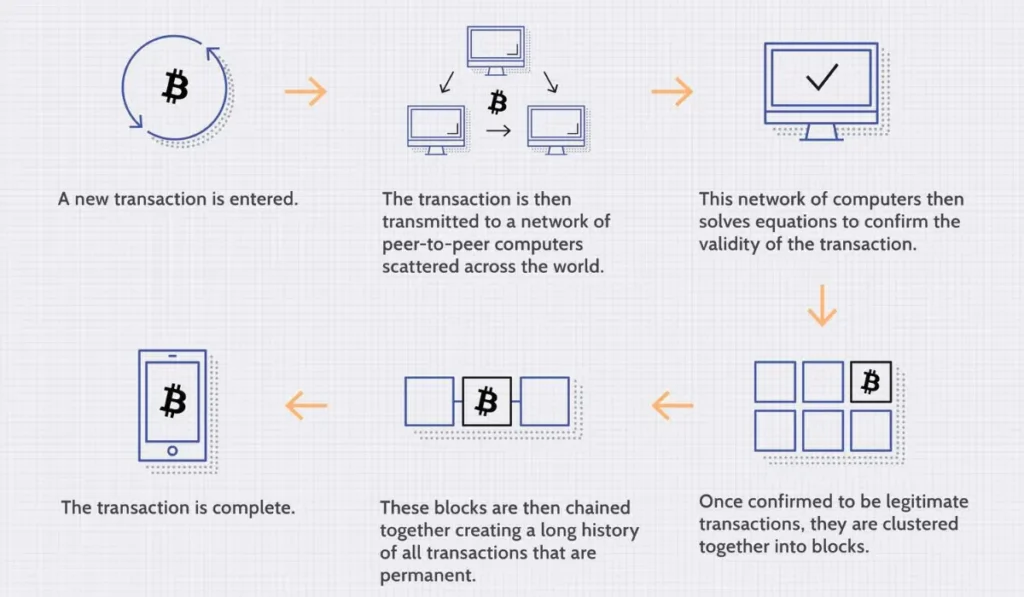
- Transaction Request: A user first initiates a transaction request, which can include cryptocurrency, contacts, records, or other data.
- Transaction broadcast: The record of the transaction is then made available to all the nodes on the network.
- Verification: Nodes communicate and cross-check the data with each other to verify the transactions.
- Waiting pools: If a transaction is verified successfully, then it is added to a waiting pool called the mempool.
- Transaction selection by miners: Different miners select the transactions from the mempool so as to incorporate them inside the blocks.
- Mining: Miners then compete to solve a cryptographic hash function to win the right to mine their block of transactions and add it to the blockchain.
- Block Addition & Cross-checking: Other nodes add the new block to their copies of the blockchain, which are then verified by cross-checking with the same block on a completely different node.
- Transaction completion: The transaction is now complete and is successfully integrated into the blockchain.
Applications of Blockchain
The blockchain is a distributed ledger. This makes it nearly impossible to modify the data in the blockchain because to accomplish this, you need to change every copy in every location. It helps to greatly improve security and transparency. All these properties of the blockchain make it ideal for a lot of scenarios. Some of its real-world use cases are given below.
- Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain facilitates seamless transactions across borders without the need for an intermediary.
- Healthcare: Blockchains are used to help secure the healthcare plans of a patient so that they can only be accessed by the primary healthcare providers with a key.
- Cryptocurrency: Blockchains are mainly used to validate transactions that take place in a crypto network.
- Internet of Things: IoT is a large network where many devices communicate and share their respective data with each other. Blockchain can be used to provide additional security to this massively distributed system.
- Asset management: In normal cases, asset management can be very expensive, especially in the case of cross-border payments. In such cases, blockchain are ideal for reducing the cost associated with it by cutting off intermediaries.
Pros & Cons of Blockchain
Blockchain is one of the top technologies in the world. However, everything has its fair share of disadvantages as well as advantages. Blockchain also has a number of advantages and disadvantages associated with it. They are listed below.
Pros:
- Security and transparency: Transactions are all recorded in a secure and distributed ledger, making them nearly impossible to tamper with.
- Decentralization: In blockchain, there is no need for intermediaries.
- Accuracy: The accuracy is greatly improved as human involvement is not required for transaction verification.
- Reduced cost: Eliminating 3rd parties results in a significant reduction of cost involved in transactions.
Cons:
- Scalability: Blockchains have a limited transaction speed. Some can only process less than 100 transactions per second, which is extremely slow.
- Energy consumption: The energy consumption associated with proof-of-work blockchains is extremely high.
- Interoperability issues: In most cases, it is extremely difficult to integrate blockchains into existing systems.
- Hacking: Blockchains are vulnerable to major cyber security threats like hacking.
- Security & privacy concerns: In some industries like healthcare, blockchains are required to address security and privacy concerns before putting them to use.
